What happens if a healthcare provider puts an ECG electrode in the wrong spot in 2025? Even small mistakes in ECG electrode placement can give wrong results. This can put patient safety and following rules in danger.
Correct placement is still very important. New technology, like wireless and wearable electrodes, is changing how we watch the heart.
-
The ECG/EKG segment remains the leading part of the medical electrode market.
-
Flexible and disposable electrodes make things more comfortable and easier to use.
-
More people need heart monitoring as the population gets older.
-
Smart electrodes that show real-time results are getting more popular with providers and patients.
Why Placement Matters
Device Accuracy
Getting the ECG reading right depends on putting electrodes in the correct places. When healthcare workers put electrodes in the right spots, the device can pick up the heart’s signals. If they make small mistakes, like putting V1 and V2 too high, the ECG pattern can change. This might make the device show fake signs of heart problems, like a septal myocardial infarction or right bundle branch block. Putting limb leads in the wrong place can also make patterns that look like heart attacks or strange rhythms. These mistakes can cause doctors to make wrong choices and give treatments that are not needed. The way the electrode touches the skin and the kind of electrode, like embroidered or gel, also matter for getting a good signal. Good placement and the right type of electrode can help the device be right almost 95% of the time.
Compliance
Healthcare workers have to follow strict rules for where to put ECG electrodes. Groups that make the rules want everyone to use the same spots so results are always good. Reading an ECG the right way depends on putting electrodes in the right places, especially when someone is very sick. Doctors use these readings to find arrhythmias and heart attacks. Following the rules helps hospitals and clinics meet standards and pass checks. Sticking to the rules also helps get devices approved and keeps them following world standards.
Patient Safety
Putting electrodes in the right place keeps patients safe. If electrodes are put in the wrong spots, the ECG might show patterns that do not match the real heart activity. This can make doctors get the wrong idea, wait too long to help, or give treatments that could hurt. The table below shows what some studies found:
|
Study / Author |
Key Findings |
Impact on Patient Safety |
|---|---|---|
|
Rajaganeshan et al. (2008) |
90% of cardiac technicians, 49% of nurses, 31% of non-cardiologist doctors, and 16% of cardiologists put V1 in the right place; V5 and V6 were often put in the wrong spot |
Putting electrodes in the wrong place can make the ECG hard to read, which can lead to the wrong treatment |
|
Medani et al. (2018) |
Only 10% put all leads in the right place; common mistakes were V1 and V2 too high, V5 and V6 too close to the middle |
Bad placement can cause wrong or late treatment because the ECG is not right |
|
McCann et al. (2007) |
Senior emergency doctors put chest electrodes in different places |
Not putting electrodes in the same place each time makes it hard to get the same results and can risk safety |
|
Walsh (2018) |
Putting V1 and V2 in the wrong place can make the ECG look like there are problems, such as incomplete right bundle branch block, T wave changes, septal Q waves, or ST-segment elevation |
Wrong ECG patterns can make doctors give the wrong treatment or wait too long, which can hurt patients |
|
Observational study on paramedics |
Many chest electrodes were put in the wrong place; many did not use the right spots on the body |
Putting electrodes in the wrong place can make the ECG look strange, which can lead to wrong or late treatment or even unnecessary trips to the hospital |
These studies show that mistakes in where electrodes go happen a lot and can be dangerous for patients. Making sure electrodes are always put in the right place helps keep patients safe and leads to better care.
ECG Electrode Placement Guidelines
3-Lead
A 3-lead ECG system uses three electrodes. These are the Right Arm (RA), Left Arm (LA), and Left Leg (LL). They show bipolar leads I, II, and III. For better results, healthcare workers put these electrodes on the chest wall. They place them the same distance from the heart. This is better than putting them on the arms or legs. It helps get a stronger signal and less movement noise.
-
RA: On the right chest, just under the collarbone.
-
LA: On the left chest, just under the collarbone.
-
LL: On the left lower chest, below the ribs.
The skin must be clean and dry before putting on electrodes. If there is hair, shaving the spot can help. Limb electrodes go on first. Chest electrodes go on after if needed. Wires for limb leads are longer. They should not mix with chest lead wires. This setup gives clear signals and good readings.
Tip: Putting 3-lead electrodes in the same spots each time helps stop wrong readings. It also helps doctors watch the heart during travel or checkups.
5-Lead
A 5-lead ECG system gives more details than a 3-lead. It uses four limb electrodes and one chest electrode. The usual spots follow world rules:
-
RA: Under the right collarbone, near the shoulder.
-
LA: Under the left collarbone, near the shoulder.
-
RL: Right lower chest, just under the ribs.
-
LL: Left lower chest, just under the ribs.
-
Chest (V): At a certain spot between the ribs, often V1 or V5.
Finding body landmarks, like the top of the breastbone, is important. The skin should be clean, dry, and not oily. Press around the edge of the electrode, not on the gel. This stops air bubbles and keeps the signal strong.
-
Lead I: Electrodes go under both collarbones.
-
Lead II and III: Electrodes go on the left leg and arms.
-
aVR and aVL: On the right and left arms.
Putting electrodes in the right place stops the ECG from looking strange. It also lowers the chance of a wrong diagnosis. The American Heart Association says to put limb electrodes on the arms and legs. Do not put them on wrists or ankles. This helps get the best results. Sometimes, putting electrodes on the chest can help with movement. But this can change the ECG pattern. If you do this, you must write down the change.
12-Lead
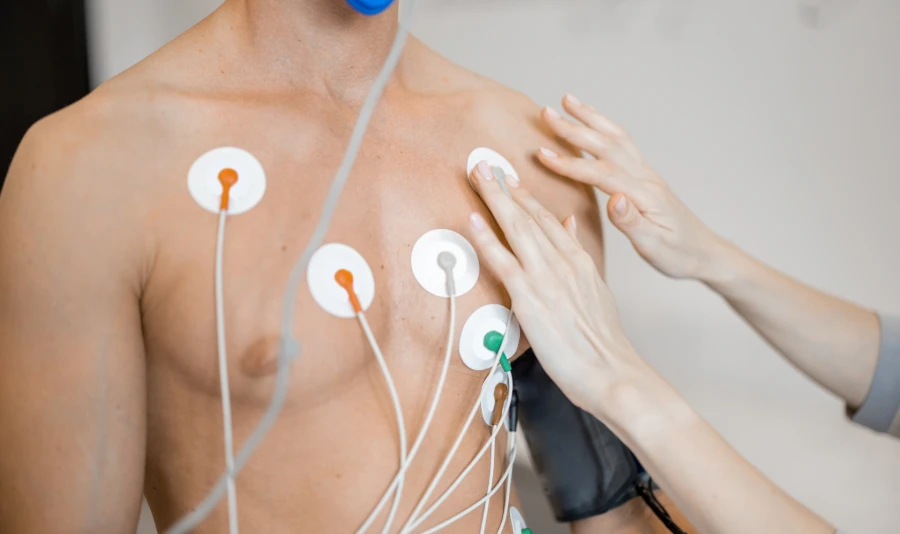
A 12-lead ECG gives the most information about the heart’s activity. It uses six limb electrodes and six chest electrodes. Putting them in the right place is very important.
|
Lead |
Placement Location |
|---|---|
|
RA |
Right arm, just under the collarbone |
|
LA |
Left arm, just under the collarbone |
|
RL |
Right leg, lower body |
|
LL |
Left leg, lower body |
|
V1 |
Fourth space between ribs, right of the breastbone |
|
V2 |
Fourth space between ribs left of the breastbone |
|
V3 |
Between V2 and V4 |
|
V4 |
Fifth space between ribs, middle of the collarbone line |
|
V5 |
Same level as V4, front armpit line |
|
V6 |
Same level as V4, middle armpit line |
Putting electrodes in the right spots helps measure the QRS axis. It also helps find heart problems like myocardial infarction. Studies show that wrong placement can change test results. This makes the test less reliable. Finding ST segment changes, like during stress tests, needs good placement. Some special lead systems can help with arrhythmias. However, they do not work as well as the standard 12-lead ECG.
2025 Updates
New updates in 2025 say skin care and patient position are very important. The skin should be dry, have no hair, and be free of oil. Using the same brand of electrodes and fresh gel helps the signal. Turn off extra electrical devices. Do not let cables make loops. Check cables for any damage. Make sure the cables and ECG device are connected well.
Studies from late 2024 and early 2025 show many electrodes are still put in the wrong place. Nurses put leads in the wrong spot 64% of the time. Cardiologists put V1 and V2 in the right spot less than 20% of the time. These mistakes can cause false results, like showing ST elevation when it is not real. This can lead to a wrong diagnosis. To fix this, a new FDA-registered product, the EXG Radiolucent Electrode System, was made. It puts all 10 electrode spots into one sticky device. This makes placement better, does not block X-rays, and works during CPR.
Note: Using the same color codes and clear labels is still very important. Most systems use these colors:
RA: White
LA: Black
RL: Green
LL: Red
Chest leads: Brown
Using the same spots and colours helps stop mistakes. It also helps follow world rules. Doing this makes sure ECG electrode placement is right, helps get approval, and keeps patients safe.